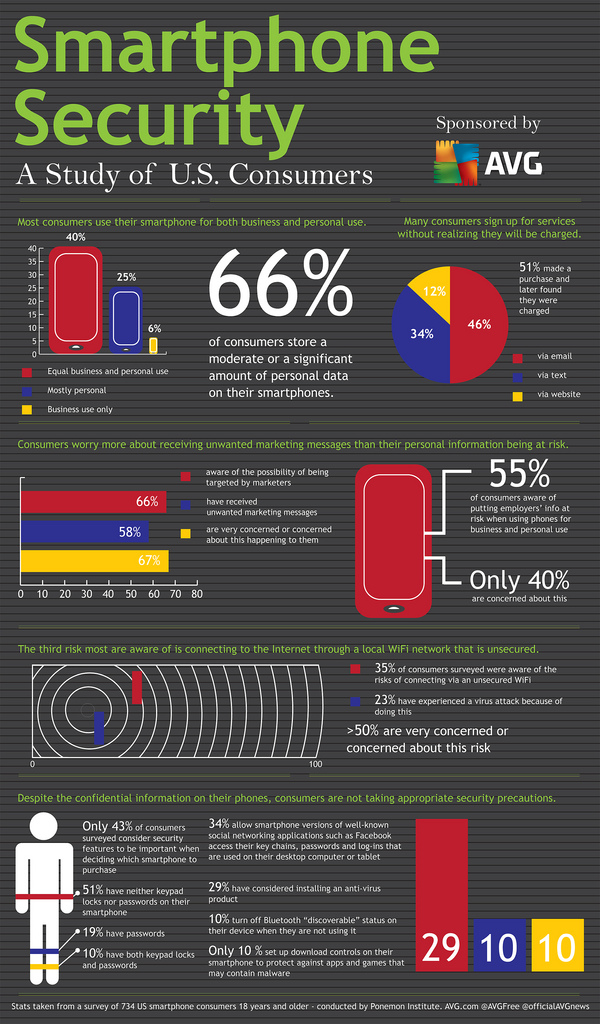
Research Groups
Malware Analysis and Secure Systems Design
The dream of designing secure systems that pass the Turing test has driven the common practice of generic exploitable software using adversarial machine learning in recent years. In order to mitigate the arms race that cannot be adapted to the present IoT infrastructure, we attempt to conceptually understand adversarial machine learning and its implications on security-centric systems, and revolutionize the way that systems are built and maintained. Our research has two interrelated thrusts: 1) understand and model the human behaviors and motivations; 2) simulate known and unknown attacks in the altered environment and securely achieve maximal success rates at the lowest resource cost. We ultimately wish to provide a foundation for developing sustainably-secure systems in the face of evolving cyber-maneuvers.
Related papers
- Sen Chen, Minhui Xue, Zhushou Tang, Lihua Xu, and Haojin Zhu, “StormDroid: A Streaminglized Machine Learning-Based System for Detecting Android Malware”, ACM ASIA Conference on Computer and Communications Security (ASIACCS), 2016. (Acceptance Rate: 73/350 = 20.9%)
- Lingling Fan, Minhui Xue, Sen Chen, Lihua Xu, Haojin Zhu, “POSTER: Accuracy vs. Time Cost: Detecting Android Malware through Pareto Ensemble Pruning”, ACM Conference on Computer and Communications Security (CCS), 2016.
Smartphone and Network Security Group
With the skyrocketing popularity of Smartphones, more and more security and privacy problems are exposed to the public. Malicious applications may overcharge users, cause extra network traffic or stole personal information. People's property and privacy are being threatened.
Our group is located in NSEC Lab and the advisor is Prof. Haojin Zhu. Our research focus on the security and privacy problem in smartphone. Below are some projects of our group:
- Profile-aware location privacy preserving platform
- Privacy attacking model in mobile social network
- Static analysis framework for security and privacy detection
Current Member:
Zhushou Tang, Jiafa Liu, Shen
Zhang, Mingli Wu, Huaxin Li
Social Network Security

The recent success of User-Review Social Networks (URSNs), like Yelp and Dianping.com, has garnered an increasing possibility to be exposed to Sybil attacks that post fake reviews to perturb the reputation of online businesses or products. Our research targets at detecting Sybil users in the URSNs by combing user mobility pattern and basic user behaviour features, since, for URSNs whose businesses generally have certain location information, the businesses reviewed by Sybil users are determined by requirements from hyping businesses and yet normal users have a predictable mobility pattern. Different with previous work, our approach has a good performance in location-based URSNs. Our further work is focusing on a novel type of Sybil users in USRNs.
Related work:
-
Xiaokuan Zhang, Haizhong Zheng, Xiaolong Li, Suguo Du, and Haojin Zhu. "You are where you have been: Sybil detection via geo-location analysis in OSNs." In Global Communications Conference (GLOBECOM), 2014 IEEE, pp. 698-703. IEEE, 2014.
Smart Vehicular System
Smart Vehicular System aims to improve the safety and comfort of drivers by exploiting data collected through massive sensors installed on the vehicle and exchanged with other vehicles or infrastructures through wireless communication. However, connecting wireless-enabled vehicles to external entities can make vehicles vulnerable to various security threats.
Our research focuses on the security and privacy problem in Smart Vehicular System:
-
Security modeling and analysis on intra vehicular network
-
Privacy risk analysis in different vehicular applications and privacy preserving framework
Take Over Intelligent Hardware(TOIH) Group
Submitted bugs on WooYun:
- 2016-04-28, 12306某站远程命令执行
- 2016-04-28, 中国人保财险某分公司命令执行
- 2016-04-28, 和讯网存在s2032命令执行漏洞
- 2015-12-22, 斐讯某主推路由器存在敏感信息泄露
Cognitive Radio Security
- Location Privacy in Database-driven Cognitive Radio Networks: Attacks and Countermeasures, Zhaoyu Gao, Haojin Zhu, Yao Liu, Muyuan Li and Zhenfu Cao, IEEE INFOCOM'13, 2013.
- Shuai Li, Haojin Zhu, Zhaoyu Gao, Xinping Guan and Kai Xing, YouSense: Mitigating Entropy Selfishness in Distributed Collaborative Spectrum Sensing, IEEE INFOCOM'13, Main Conference, 2013.
- Sheng Liu, Haojin Zhu, Rong Du, Cailian Chen, Xinping Guan, Location Privacy Preserving Dynamic Spectrum Auction in Cognitive Radio Network, IEEE ICDCS'13, Main Conference, 2013.
- Security and Privacy of Collaborative Spectrum Sensing in Cognitive Radio Networks, Zhaoyu Gao, Haojin Zhu, Shuai Li, Suguo Du and Xu Li, IEEE Wireless Communications, vol.19, no.6, 2012.
- Location Privacy Preservation in Collaborative Spectrum Sensing, Shuai Li, Haojin Zhu, Zhaoyu Gao, Xinping Guan, Kai Xing and Xuemin (Sherman) Shen, INFOCOM 2012, Orlando, Florida USA, March 25-30, 2012.